예외처리 하는 방법임.
오류가 날것같은 코드에 try ~ catch 문을 씌워서 에러가 나면 catch를 실행하게 하는 방법이다.
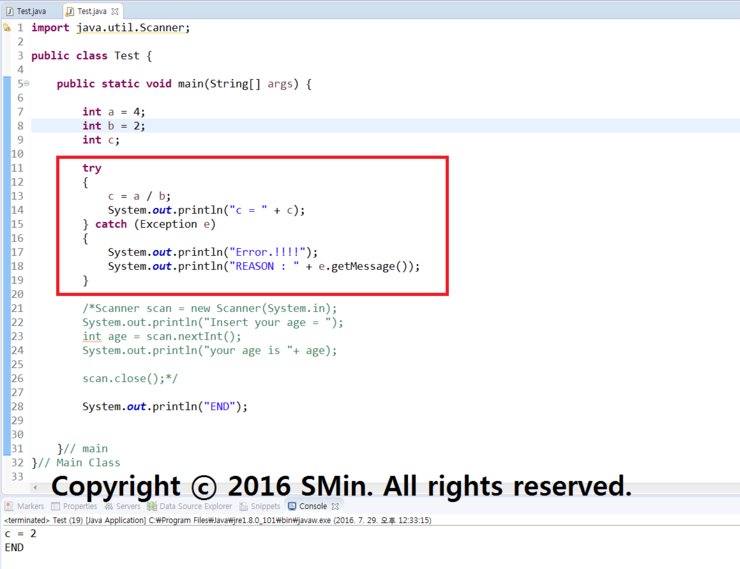
00. 간단하게 나누기로 예를 들었다. try~catch문을 써서 실행하면 일반 출력값과 차이가 없음을 볼 수 있다.
01. 하지만, b값에 0을 두면 에러가 나기때문에 catch쪽으로 넘어가게 된다.
이때, 'e.getMessage();' 를 쓰게되면 에러 이유가 나오게 된다.

02. 'e.printStackTrace();' 를 사용하면 이유와 설명등을 함께 볼 수 있다.

03. 결과값. 해석하면 바운더리를 초과했다는 뜻이다.
우리가 배열을 만들때 6개 짜리를 만들었으니 0~5 만큼 인데
[6] 자리에 3을 넣으려고 하니 6자리가 없다고 에러가 난 것이다.

※. 코드
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 4;
int b = 2;
int c;
int[] lotto = new int[6];
try
{
c = a / b;
System.out.println("c = " + c);
lotto[6] = 3;
} catch ( ArithmeticException e )
{
System.out.println("Error.!!!!");
System.out.println("REASON : " + e.getMessage());
} catch ( Exception e1 )
{
System.out.println("REASON : " + e1.getMessage());
e1.printStackTrace();
} finally // try~catch 가 끝났음을 알릴 수 있다. 파일처리에서 유용함.
{
System.out.println(" OK Try ~~ Catch ");
}
/*Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Insert your age = ");
int age = scan.nextInt();
System.out.println("your age is "+ age);
scan.close();*/
System.out.println("END");
}// main
}// Main Class
