ㅁ. 01로 이루어진 바이너리 파일 처리하기.
이전 I/O처리와 비슷하니 아래 링크에서 참조바람.
ㅁ. 코드는 다음과 같다.
>
02. 결과값 스트링으로 나오는 것을 확인 할 수 있다.
>

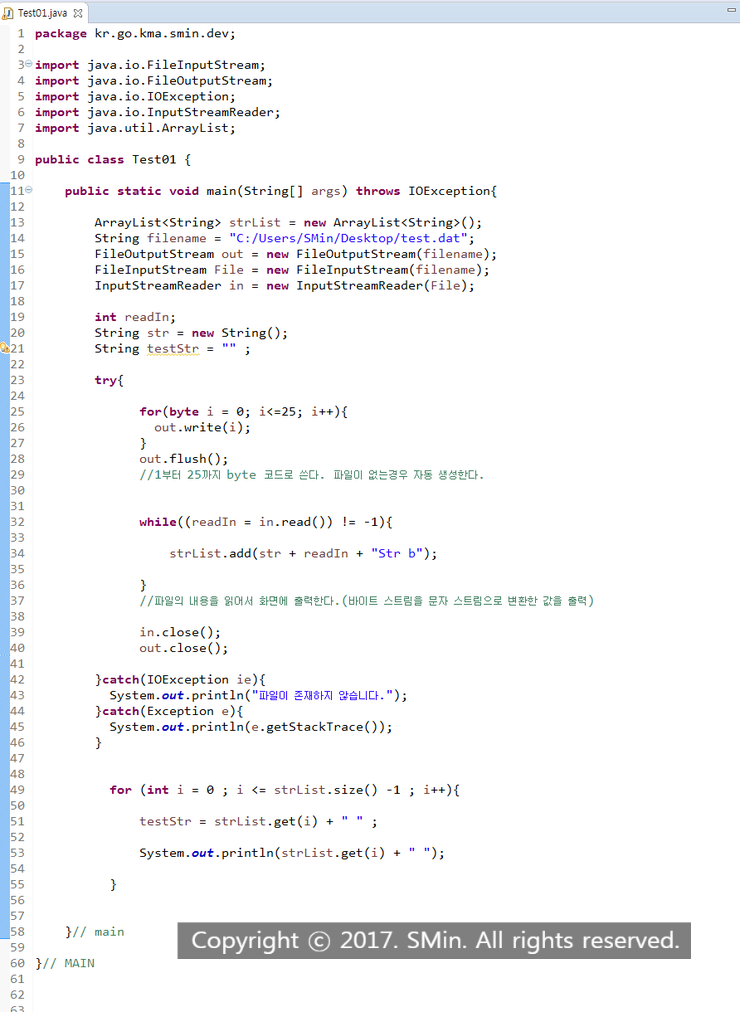
※. 코드
>
package kr.go.kma.smin.dev;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
ArrayList<String> strList = new ArrayList<String>();
String filename = "C:/Users/SMin/Desktop/test.dat";
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(filename);
FileInputStream File = new FileInputStream(filename);
InputStreamReader in = new InputStreamReader(File);
int readIn;
String str = new String();
String testStr = "" ;
try{
for(byte i = 0; i<=25; i++){
out.write(i);
}
out.flush();
//1부터 25까지 byte 코드로 쓴다. 파일이 없는경우 자동 생성한다.
while((readIn = in.read()) != -1){
strList.add(str + readIn + "Str b");
}
//파일의 내용을 읽어서 화면에 출력한다.(바이트 스트림을 문자 스트림으로 변환한 값을 출력)
in.close();
out.close();
}catch(IOException ie){
System.out.println("파일이 존재하지 않습니다.");
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getStackTrace());
}
for (int i = 0 ; i <= strList.size() -1 ; i++){
testStr = strList.get(i) + " " ;
System.out.println(strList.get(i) + " ");
}
}// main
}// MAIN