'ETC > 먹방' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 2019. 08. 08. 목. 저녁. (0) | 2019.08.08 |
|---|---|
| 2019. 08. 07. 수. 저녁. (0) | 2019.08.07 |
| 2019. 08. 01. 목. 저녁. (0) | 2019.08.02 |
| 2019. 07. 31. 수. 저녁. (0) | 2019.07.31 |
| 2019. 07. 28. 일. 점심 (0) | 2019.07.28 |
| 2019. 08. 08. 목. 저녁. (0) | 2019.08.08 |
|---|---|
| 2019. 08. 07. 수. 저녁. (0) | 2019.08.07 |
| 2019. 08. 01. 목. 저녁. (0) | 2019.08.02 |
| 2019. 07. 31. 수. 저녁. (0) | 2019.07.31 |
| 2019. 07. 28. 일. 점심 (0) | 2019.07.28 |
Throw 예외처리 하는 방법임.
ㅁ. 간단할 설명.
'divide();' 에서 일을 다 처리하기 때문에 정작 메인에서는 알 수가 없다.
따라서, 'divide2();' 에서 작업을 시킨다음에 그 작업내역을 메인으로 던져서(throw) 메인에서 일(TryCatch)을 할 수 있게 한다.
00. 'divide(){}' 를 평소처럼 만들고 'divide2(){}' 는 만들때 throws Exception을 써서 만들어보자.
하지만, 메인메소드에 적을때에는 'divide2();' 를 try~catch 내부에 넣어야 함을 잊지말자.

01. 결과값.

※. 코드
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
divide();
try {
divide2();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println("main Reason : " + e.getMessage());
}
}
public static void divide2() throws Exception
{
int a = 2;
int b = 0;
int result;
result = a/b;
System.out.println("result = " + result);
}
public static void divide()
{
int a = 2;
int b = 1;
int result;
try {
result = a/b;
System.out.println("result = " + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println("Reason : " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
Thread(동시동작, 멀티태스킹) 사용방법.
ㅁ. 쓰레드는 일반적으로
1. Thread 클래스를 상속받아서 사용하는 경우
; 자바가 단일상속만 허용하기 때문에 Thread를 상속받는 순간 다른 클래스를 이용할 수 없어서,
사용에 제한이 있을 수 있다.
2. Runnable interface를 구현하는 방법이 있다.
; interface를 사용하기 때문에, 필요한 경우에 다른 클래스를 상속받아서 사용할 수 있다.
따라서, 일반적으로는 Runnable interface를 구현하는 방법으로 사용한다.
00. Runnable 인터페이스를 implements 하면 run()메소드를 오버라이드 해야한다.
run()메소드안에 구동될 코드를 작성하면 된다.

01. 메인 클래스에 객체를 생성하고 생성한 객체를 쓰레드속에 넣어서 구동 '.start();' 시켜주면된다.

02. 1,3,5초에 맞춰서 각각 작동됨을 확인할 수 있다.

예외처리 두번째 방법임.
ㅁ. 간단할 설명.
'readMessage();' 에서 일을 다 처리하기 때문에 정작 메인에서는 알 수가 없다.
따라서, 'readMessage2();' 에서 작업을 시킨다음에 그 작업내역을 메인으로 던져서(throw) 메인에서 일(TryCatch)을 할 수 있게 한다.

01.
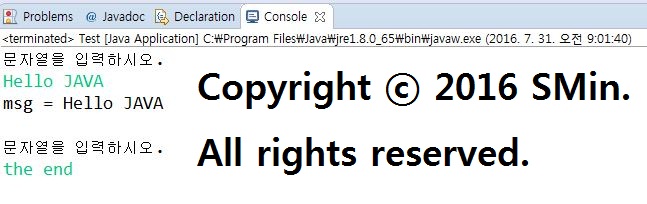
※. 코드
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String msg;
// 호출당한 readMessage()에서 예외처리
msg = readMessage();
System.out.println("msg = " + msg);
// readMessag2() 문제발생하면 처리하지 않고,
// 나한테 알려만 주기때문에,
// 내가 예외 처리해줌.
try {
msg = readMessage2();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Reason : " + e.getMessage());
}
}// main
// 호출 당한 함수는 문제가 발생하면 처리하지 않고,
// 나를 호출한 함수한테 알려주는 방법.
public static String readMessage2() throws IOException
{
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
System.out.println("문자열을 입력하시오.");
System.in.read(buffer);
return new String(buffer);
}
// 호출을 당한 함수가 예외 처리하는 경우
public static String readMessage()
{
//return "Hello ~~";
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
System.out.println("문자열을 입력하시오.");
// 키보드의 입력은 OS는 모두 파일로 인식
try {
System.in.read(buffer);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Reason : " + e.getMessage());
}
return new String(buffer);
}
}// Main Class
예외처리 하는 방법임.
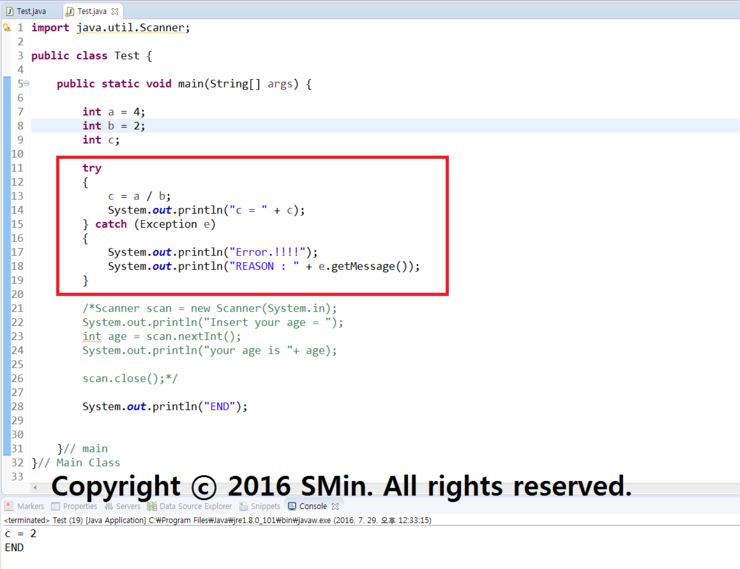
오류가 날것같은 코드에 try ~ catch 문을 씌워서 에러가 나면 catch를 실행하게 하는 방법이다.
00. 간단하게 나누기로 예를 들었다. try~catch문을 써서 실행하면 일반 출력값과 차이가 없음을 볼 수 있다.
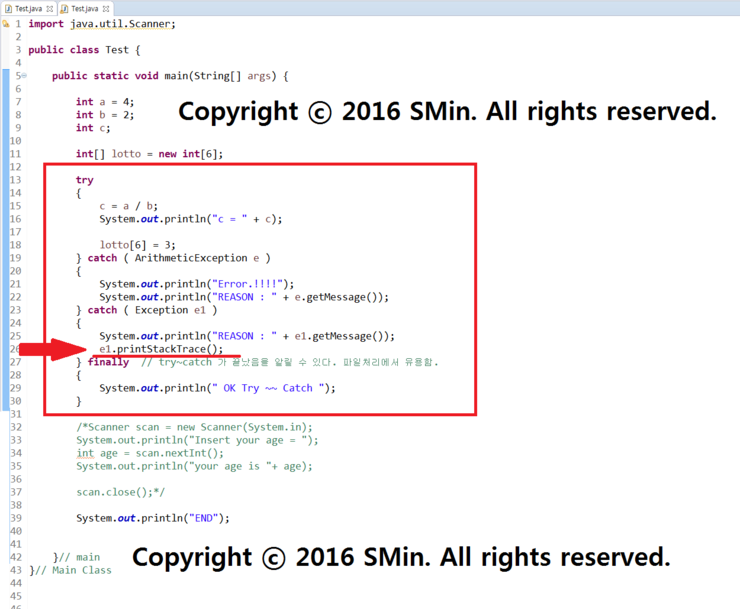
01. 하지만, b값에 0을 두면 에러가 나기때문에 catch쪽으로 넘어가게 된다.
이때, 'e.getMessage();' 를 쓰게되면 에러 이유가 나오게 된다.

02. 'e.printStackTrace();' 를 사용하면 이유와 설명등을 함께 볼 수 있다.
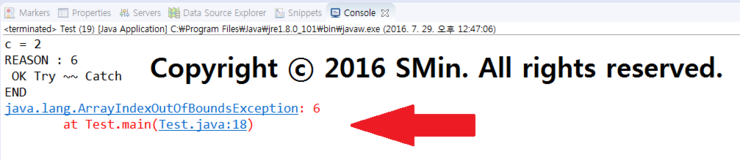
03. 결과값. 해석하면 바운더리를 초과했다는 뜻이다.
우리가 배열을 만들때 6개 짜리를 만들었으니 0~5 만큼 인데
[6] 자리에 3을 넣으려고 하니 6자리가 없다고 에러가 난 것이다.
※. 코드
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 4;
int b = 2;
int c;
int[] lotto = new int[6];
try
{
c = a / b;
System.out.println("c = " + c);
lotto[6] = 3;
} catch ( ArithmeticException e )
{
System.out.println("Error.!!!!");
System.out.println("REASON : " + e.getMessage());
} catch ( Exception e1 )
{
System.out.println("REASON : " + e1.getMessage());
e1.printStackTrace();
} finally // try~catch 가 끝났음을 알릴 수 있다. 파일처리에서 유용함.
{
System.out.println(" OK Try ~~ Catch ");
}
/*Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Insert your age = ");
int age = scan.nextInt();
System.out.println("your age is "+ age);
scan.close();*/
System.out.println("END");
}// main
}// Main Class